BSc Botany 1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes 2024 .BSc Botany or Bachelor of Science in Botany is a 3-year undergraduate degree course, which deals with the study of plants and their physiology. Notes.The Notes of BSc 1st year is divided into two semesters, i.e. Sem I & Sem-II. Below is the complete semester wise syllabus of BSc Botany. BSc Botany Semester BSc.BSc Botany 1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes 2024 .
Principles of Biochemistry Notes
biochemistry, study of the chemical substances and processes that occur in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Biochemistry may be use to study the properties of biological molecules, for a variety of purposes. For example, a biochemist may study the characteristics of the keratin in hair so that shampoo develop that enhances curliness or softness. Biochemists find uses for biomolecules.
How is biochemistry use in everyday life?
It is used in clinical diagnosis, manufacturing of various biological products, treatment of diseases, in nutrition, agriculture, etc. … Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are the most common biological molecules studied by biochemists. Biochemistry also encompasses the science of molecular biology.
What are the three types of biochemistry?
A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines.
| Principles of Biochemistry – 1st part | Download View |
| Principles of Biochemistry – 2nd Part | Download View |
| Principles of Biochemistry – 3rd Part | Download View |
How many branches of biochemistry are there?
The other branches include Animal and Plant Biochemistry, Biotechnology, Molecular Chemistry, Genetic engineering, Endocrinology, Pharmaceuticals, Neurochemistry, Nutrition, Environmental, Photosynthesis, Toxicology, etc.
What are the 7 branches of biochemistry?
What are the Branches of Biochemistry ?
- Structural biochemistry.
- Bio-organic Chemistry.
- Enzymology.
- Metabolic Biochemistry.
- Xenobiotics.
- Immunology.
- Endocrinology.
- Neurochemistry.
Who studies biochemistry?
Biochemists and biophysicists study the chemical and physical principles of living things and of biological processes, such as cell development, growth, heredity, and disease.
Different types of Chemistry
Fundamentally, chemistry is the study of matter and change. The way that chemists study matter and change and the types of systems that are studied varies dramatically. Traditionally, chemistry has been broke into five main subdisciplines: Organic, Analytical, Physical, Inorganic, and Biochemistry. Over the last several years, additional concentrations have begun to emerge, including Nuclear chemistry, Polymer chemistry, Biophysical chemistry, Bioinorganic chemistry, Environmental chemistry.
BSc Botany 1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes
All of these areas of chemistry are address in our classes here at UWL to some extent, and by the research interests of our faculty in the Chemistry Department. The following descriptions of the five major subdisciplines were write by several of our faculty members in their field of expertise. All of our faculty members would be happy to elaborate, and/or discuss other aspects of chemistry that are not describe below! UW-La Crosse’s accredited Chemistry and Biochemistry programs blend technical, hands-on research experience with practical skill development.
1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes
Also, understanding something about organic chemistry is essential for learning about biochemistry and molecular biology because bio-molecules such as proteins, sugars, fats, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are all organic molecules, albeit very large ones. Students who concentrate in organic chemistry typically go on to work in pharmaceutical, food or polymer companies, do research or teach in organic chemistry, pursue medical careers, or may pursue other related job opportunities. BSc Botany 1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes .
BSc Botany 1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes
A lot of the current physical chemistry research in industry and academia combines the techniques and ideas from several fields. For example, some chemists apply physical chemistry techniques to investigations of the mechanisms of organic reactions (what collisions and bond rearrangements occur, how fast are they, how many steps are there, etc.) – this type of study is called physical organic chemistry. Others apply physical techniques to the study of biological systems (why do proteins fold into the shapes that they have, how is structure related to function, what makes a nerve work, etc.) – this type of study is biophysical chemistry. Still others may use physical techniques to characterize polymers or study environmental systems. BSc Botany 1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes .
BSc Botany 1st year Principles of Biochemistry Notes
In all of these cases, physical chemists try to understand what is happening on an atomic level, and why. Students who concentrate in physical chemistry may go onto pursue careers in industry, research or teaching. A lot of the current physical chemistry research in industry and academia combines the techniques and ideas from several fields. Bioinorganic chemists study the function of metal-containing compounds within living organisms.
Principles of Biochemistry Notes
In all of these cases, physical chemists try to understand what is happening on an atomic level, and why. Students who concentrate in physical chemistry may go onto pursue careers in industry, research or teaching. A lot of the current physical chemistry research in industry and academia combines the techniques and ideas from several fields.
Graphics Legend:
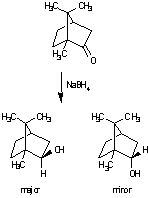
Organic chemistry: Reduction of camphor by sodium borohydride.
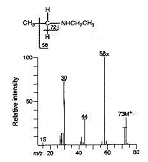
Analytical chemistry: Mass spectrum of diethylamine.
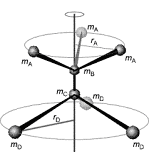
Physical chemistry: Illustration of the moment of inertia of a molecule such as ethane.
Inorganic chemistry: X-ray crystal structure of a novel solid state inorganic compound synthesized by Dr. Rob McGaff’s research group.
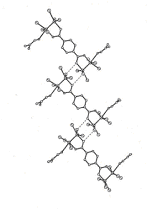
Biochemistry: Schematic drawing showing the structural elements of lactate dehydrogenase domain I.
