Plant Physiology 6th Semester Past Paper 2023 All University.Plant Physiology 6th Semester Past Paper 2023 All University.Plant Physiology 6th Semester Past Paper 2024 All University.
| Past Paper | View |
|---|---|
| Mid Term Past Paper Plant Physiology pdf | Download _View |
| Mid Term Past Paper Plant Physiology pdf Short Answer | Download _View |
| Mid Term Past Paper Plant Physiology Answers pdf | Download _View |

Difference Between Respiration Krebs Cycle and Glycolysis ?
| Respiration | Krebs Cycle | Glycolysis |
|---|---|---|
| The process of respiration in plants involves using the sugars produced during photosynthesis plus oxygen to produce energy for plant growth. | Krebs Cycle is a sequence of reactions in the living organism in which oxidation of acetic acid or acetyl equivalent provides energy for storage in phosphate bonds (as in ATP) — called also citric acid cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle. | Glycolysis is defined as breakdown of glucose is called Glycolysis |
| In many ways, respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis. In the natural environment, plants produce their own food to survive. | The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle, | Glycolysis is a cytoplasmic pathway which breaks down glucose into two three-carbon compounds and generates energy. |
Respiration occurs when glucose (sugar produced during photosynthesis) combines with oxygen to produce useable cellular energy. This energy is used to fuel growth and all of the normal cellular functions. | This process is called the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle consumes pyruvate and produces three things: carbon dioxide, a small amount of ATP, and two kinds of reductant molecules called NADH and FADH. The CO2 produced by the Krebs cycle is the same CO2 that you exhale. | Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose, into pyruvic acid. |
Difference Between Oxygenic and Anoxygenic Photosynthesis ?
| Oxygenic Photosynthesis | Anoxygenic Photosynthesis |
|---|---|
| oxygenic photosynthesis produces oxygen as a by product | Anoxygenic photosynthesis does not produce oxygen as a by product. |
| Occurs in plant , algae and Cycnobacteria | occurs in the green sulfur and nonsulfur bacteria, purple bacteria, heliobacteria and acidobacteria. |
| Both Photosystem 1 and 2 are used | Only photosystem I is used in the anoxygenic photosynthesis. |
| Water is the electron source. | Hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide or ferrous ions serves as the electron donor in anoxygenic photosynthesis. |
| Oxygen is produced during the light reaction. | Oxygen is not produced during the light reaction in anoxygenic photosynthesis. |
| Chlorophylls are used | Bacteriochlorophylls or chlorophylls are used in anoxygenic photosynthesis. |
| NADP serves as the terminal electron acceptor, producing NADPH in oxygenic photosynthesis. | NADPH is not produced in anoxygenic photosynthesis as the electrons are cycled back to the system. |
| ATP is produced by noncyclic photophosphorylation | ATP is produced by cyclic photophosphorylation |

Similarities Between Oxygenic and Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
- Oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis are two types of photosynthesis.
- Photoautotrophs undergo both oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis.
- Both oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis occurs in two steps: light dependent reaction and dark reaction.
What is Oxygenic Photosynthesis ?
Oxygenic photosynthesis refers to the photosynthesis that occurs in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria in which the final electron acceptor is water. It occurs in two steps: light reaction and dark reaction. The light-trapping pigments used in oxygenic photosynthesis are chlorophyll A and B. The energy trapp by chlorophyll A is pass to the photosystem II (PS II) (P680) and photosystem I (PS I) (P700) in the form of high energy electrons. PS II takes electrons by splitting water molecules into molecular oxygen, generating high energy electrons, which are transfer through a series of electron carriers into PS I.
Splitting of water at PS II is call photolysis. PS I also generates high energy electrons by the energy of sunlight. These electrons are use in the formation of NADPH by the enzyme, NADP+ reductase. ATP synthase utilizes H+ ions, which are generate by photolysis in order to produce ATP. The overall reaction of photosynthesis is show in figure 1.
Figure 1: Oxygenic Photosynthesis
During the dark reaction of photosynthesis, glucose is produced from the energy of ATP and NADPH produced in the light reaction.
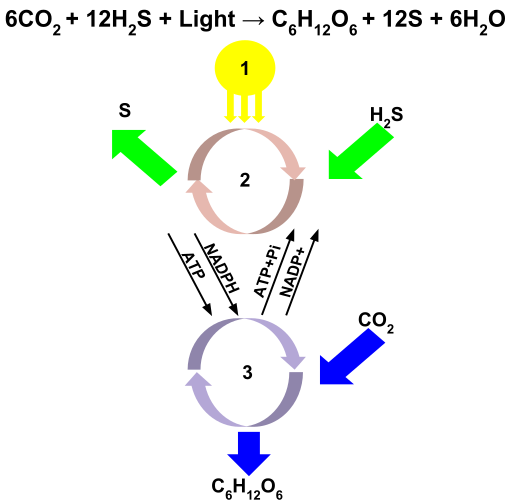
What is Anoxygenic Photosynthesis ?
Anoxygenic photosynthesis refers to the photosynthesis in bacteria that occurs under anaerobic conditions, using inorganic molecules as the electron source other than H2O. It occurs in green sulfur and nonsulfur bacteria, purple bacteria, heliobacteria, and acidobacteria. In photosynthetic bacteria, P680 is not present. H2O is too electropositive to be use as an electron source in anoxygenic photosynthesis. Based on the species of the bacteria, the type of pigments present in the PS I may differ. It can be either chlorophyll or bacteriochlorophyll. P870 is the reaction center in purple bacteria. The inorganic electron donor in the PS I may be hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide or ferrous ions. The anoxygenic photosynthesis is show in figure 2.
Figure 2: Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
Conclusion
Oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis are two types of photosynthesis. Oxygenic photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Anoxygenic photosynthesis occurs in cyanobacteria. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of oxygenic photosynthesis. However, oxygen is not produced as a byproduct of anoxygenic photosynthesis. The main difference between oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis is the ability to produce oxygen during each type of photosynthesis.
Reference:
1. “Phototrophy.” Boundless Microbiology.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Photosynthesis equation” By ZooFari – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Anoxygenic Photosynthesis in Green Sulfur Bacteria” By Lithium byproduct – Own work.